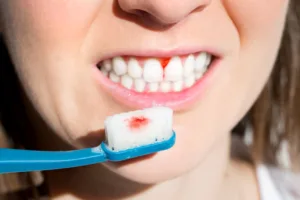
Dental care issues are the primary cause of bleeding gums. Gingivitis (inflammation of the gums) and periodontitis make your gums sensitive and prone to bleeding.
Gingivitis
Most people develop gingivitis when plaque stays on gum lines too long. Plaque refers to the debris and bacteria that stick to your teeth.
Brushing your teeth removes plaque and can prevent you from developing cavities (dental caries). But plaque may stay on your gum line, if you don’t brush and floss properly.
If plaque isn’t removed it can harden into tartar (calculus), which will increase bleeding. The accumulation of plaque near your gums can also cause gingivitis.
Symptoms of gingivitis include:
- puffy gums
- soreness in the mouth and around the gums
- bleeding gums
Periodontitis
Periodontal disease (periodontitis) can occur when gingivitis becomes advanced. Periodontal disease is an infection of the gums, jawbone, and supportive tissues that connect your teeth and gums. Periodontitis can cause your teeth to loosen or fall out.
Vitamin deficiencies
Vitamin C and vitamin K deficiencies can also cause gums to bleed easily.
Ask your doctor to check your levels of vitamins C and K if you have bleeding gums that aren’t caused by improper dental care. Also, follow a diet that contains both nutrients to ensure you’re getting the vitamins you need to stay healthy.
Foods rich in vitamin C include:
- citrus fruits and juices
- broccoli
- strawberries
- tomatoes
- potatoes
- bell peppers
Foods rich in vitamin K include:
- watercress
- kale
- spinach
- Swiss chard
- lettuce
- mustard greens
- soybeans
- canola oil
- olive oil
Other causes of bleeding gums
People who wear dentures also may sometimes experience bleeding gums. This is more likely when dentures fit too tightly.
Talk to your dentist if dentures or other oral appliances are causing your gums to bleed. They may need to take new impressions to create a better fitting mouthpiece.
Pregnancy commonly causes of gum bleeding. Hormonal changes that occur during pregnancy can cause the gums to be more sensitive.
Treatment of bleeding gums
Good dental hygiene is the first step to managing bleeding gums.Get your dental cleaning and polishing done in every six months to one year
Your dentist may also show you how to use an antiseptic mouthwash to minimize plaque that forms in your mouth. And a rinse of warm salt water can help soothe swollen gums that bleed easily.
Use a soft toothbrush. It’ll be gentle on inflamed gums, especially if you experience bleeding after brushing your teeth. Medium and hard bristles may be too abrasive for your delicate gums.
